This page is designed as a simple usage guide and beginner's course for those who are using Steinberg Cubase for the first time.
This guide assumes the following environment:
- Required Cubase: Cubase Pro 14
(Cubase must be installed and activated)
- Platform: Windows 10 Home 64bit
Although this content is a guide for Cubase 14, it should also be useful for earlier versions.
For screens that have not changed from Cubase 13, images from the "Cubase 13 Operation Guide" are reused.
Article Categories
Related information
- Below is a collection of articles about Cubase 14. Those who have used previous versions may find the information useful.
 CUBASE 14
CUBASE 14
Here we will create an empty project with basic settings.
- (1) Start Cubase
- (2) Audio driver settings
- (3) Creating a new project
- (4) Save the project and close Cubase.
- (5) Start Cubase, reload the project, and make basic settings
Here are some environmental checks that we recommend you do first.
- (1) Check that Cubase can produce sound
- (2) Check if Cubase is ready to record audio
- (3) Check if Cubase is set up to record using a MIDI keyboard
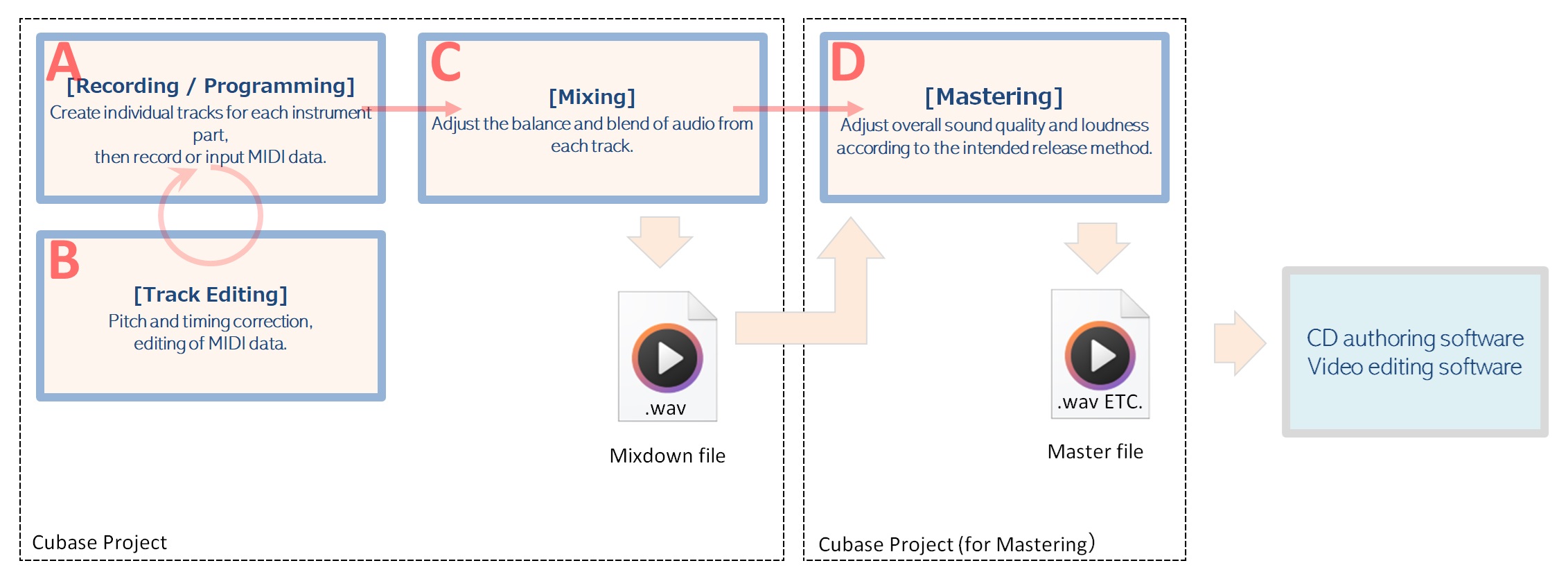
Let's learn the basics of Cubase by recording about 4 bars of music.
Here, we will use only HALion Sonic 7 as an instrument (VSTi).
- (1) Setting the tempo and MIDI recording mode
- (2) Creating a drum track and simple input (4 bars)
- (3) Creating a bass track and simple input (4 bars)
- (4) Creating a piano track and simple input (4 bars)
- (5) Creating a string track and simple input (4 bars)
- (6) You can easily operate the app (use frequently used shortcuts)
Here, we will load an audio file of an instrument (karaoke) or an original sound source for ear copying into the project and create an audio track.
- (1) Mute unnecessary tracks
- (2) Loading an audio file
- (3) Make sure the audio track can be played
Use Cubase's "Tempo Detection" to create a tempo track from your audio events.
- (1) Check that the metronome click is not in sync
- (2) Automatically generate a tempo track from audio events
- (3) Adjusting the beat
- (4) Tempo Track Editor
- (5) Delete the tempo track and the signature track in the project screen
Creates a chord track from audio events.
- (1) Create an empty chord track
- (2) Detecting chords from audio events
- (3) Play piano or strings on the chord track
Use SpectraLayers, which comes with Cubase, to separate the orchestra and vocals from the original audio source that you copied by ear.
- (1) Separate the original track and vocals using SpectraLayers
- (2) Separate the orchestra and vocals into audio tracks
- (3) Stop using SpectraLayers on the source material for ear copies
Let's try using the loops and samples that come with Cubase.
- (1) How to open loops and samples
- (2) Media Type and Preview Section Settings
- (3) How to incorporate Loops & Samples into your project
- (4) Checking after work
Here we've put together some information that may be useful for you to get started in earnest.
- (1) Using Groove Agent SE
- A. Individual drumming
- B. Entering a preset pattern
- C. Paste a preset pattern into a track and edit it
- (2) Using PadShop
- (3) Using Retrologue
- (4) How to use Folder Tracks
- (5) Stop using the lower zone on a regular basis
- (6) Edit parts (delete, cut, extend, split, move, copy, etc.)
- (7) How to improve your ear copy skills
- (8) How to record original songs
- (9) Let's say you're done typing.
Record vocals and guitar. In this example, the vocals are recorded in mono with one microphone, and the guitar is recorded in stereo through an amp simulator.
- (1) Metronome, recording mode (common, audio) and audio connection settings
- (2) Recording Vocals
- (3) Recording the guitar
 CUBASE 14
CUBASE 14